Developing new IT skills is one of the best ways to demonstrate your value as an IT director so you can advance within your organization.
Anyone can learn a new skill, and many of you have spent years cultivating valuable skills that have provided you with countless career opportunities.
To give you some ideas on where to start, here’s a list of 12 steps you can take to develop the most in-demand IT skills right now.
- Secure Your Network.
- Learn Programming.
- Understand Computer Networks.
- Master Cloud Computing.
- Focus on System and Network Administration.
- Delve into Data Analytics.
- Implement the DevOps Methodology.
- Fine-Tune Your Project Management Skills.
- Become Familiar with Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Learn Web Development.
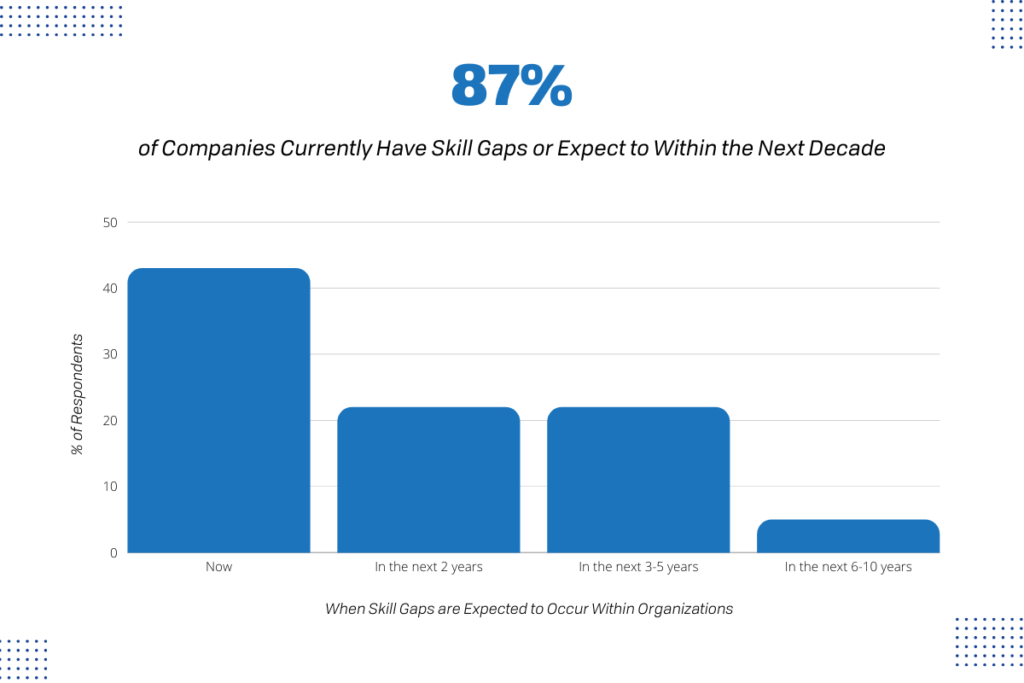
Step 1. Secure Your Network.
Security is the foundation of IT, and a knowledge of cybersecurity across various platforms will be crucial to your success as an IT director.
Knowledge of Cybersecurity Across Various Platforms
Cybersecurity isn’t just limited to computers. To become a security expert, you’ll need to be comfortable working on a variety of operating systems, computer systems, devices, and networks. You’ll also need a solid understanding of hardware and software security.
Risk Mitigation and Threat Analysis
Cybersecurity begins with understanding the risks and vulnerabilities that could negatively impact your organization. Risk identification, analysis, and management will help you identify vulnerabilities so you can better protect your company’s network and its data.
Data Encryption
Data encryption defends your organization’s data against cyber attacks. Translating data from plain text (unencrypted) to ciphertext (encrypted) ensures that only users who have the encryption key can access the data.
Penetration Testing
Think of a penetration test as a simulated cyber attack against your computer system. In the context of web application security, penetration testing is commonly used to augment a Web Application Firewall (WAF). Insights provided by the penetration test can be used to fine-tune your cybersecurity policies and patch detected vulnerabilities.
Compliance
As data privacy laws become more prevalent, it will be important for you to understand compliance regulations and standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and CCPA. Prioritizing compliance fosters trust and reduces legal problems for your organization.
Ethical Hacking
In order to effectively protect your organization’s network and infrastructure, you’ll need to know how they can be exploited in the first place. As a cybersecurity professional, you’ll need to learn how to “ethically hack” so you can fully understand how a system could be breached. This will also help you create more effective solutions for thwarting these attacks.
Step 2. Learn Programming.
Aside from cybersecurity, programming is one of the most in-demand skills in the IT industry. Programming languages touch nearly every IT job role, and coding is a crucial skill to have when it comes to software engineering and web development.
As an IT director, programming can also help you promote efficiency by automating tasks within your department.
Here are some of the most common programming languages:
- JavaScript
- Python
- Java
- C/C++
- R
- Go
- HTML
- PHP
- C#
- Ruby
Check out some of our favorite programming courses on Coursea, Udemy, Skillshare, Zero to Mastery, Codecademy, and freeCodeCamp.
Step 3. Understand Computer Networks.
Knowledge of computer networks will always be an important skill to have, whether you’re focused on network administration or network security.
Internet Protocol (IP) Configuration
Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are required by any network adapter on any computer that needs to connect to the internet or to another computer.
As the head of your IT department, you’ll need to understand how to enable Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and change the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/IP settings for the devices in your organization’s network.
Routing Configuration
In addition to IP configuration, you’ll need to be able to configure your organization’s routers and other devices.
Routing configuration involves adding a default route, adding routes to networks that aren’t directly connected, and adding routes to networks that can be reached through route-based VPNs.
Hardware and Software Configurations
Finally, it’s important for you to be able to configure the hardware and software necessary for your organization to function.
Hardware configuration refers to the system resource settings assigned to a specific device.
Software Configuration Management (SCM) is the process of managing and controlling changes in software.
Step 4. Master Cloud Computing.
Cloud computing has been listed as one of the most in-demand IT skills for years. This includes everything from end user support to deploying and maintaining cloud platforms.
Cloud Technologies and Platforms
At minimum, it’s important for you to have a solid understanding of at least one of the leading cloud providers:
- Microsoft Azure
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- CloudLinux
Ideally, you should be able to demonstrate multi-platform expertise, spanning your knowledge over several cloud platforms. This breadth of knowledge will give you an edge in the job market, and it will also enable you to manage cloud computing more effectively within your IT department.
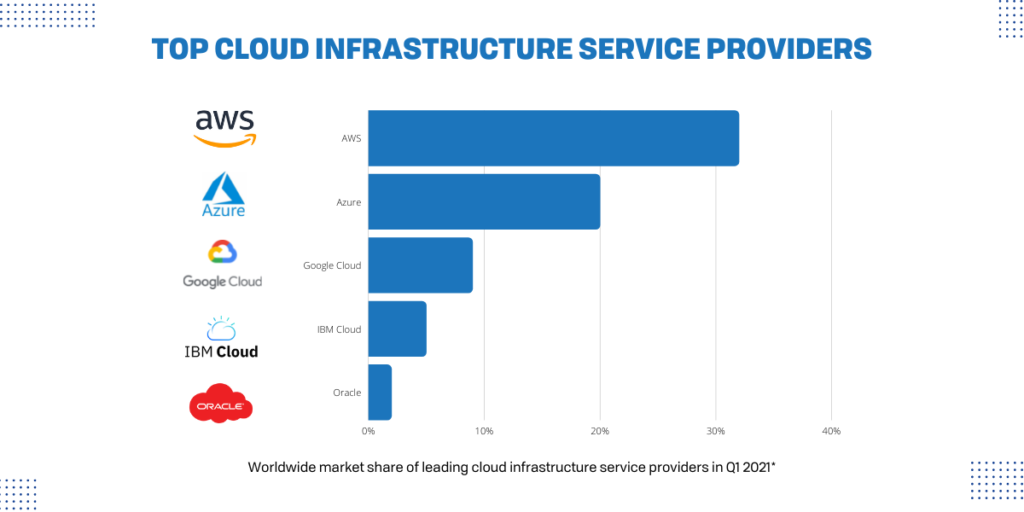
Types of Cloud Computing
Not all clouds are the same, and one type of cloud computing might not be the right fit for everyone.
Here are the three most common types of cloud computing architecture:
- Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers, which deliver their computing resources, like cloud servers and data storage, over the internet. With the public cloud, all hardware, software, and supporting infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider.
- Private clouds are hosted and maintained on a private network, and their cloud computing resources are exclusive to a single organization. A private cloud might be physically located on the company’s on-site datacenter, or they might pay a third-party service to host their private cloud.
- Hybrid clouds combine public and private through technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. This allows your organization greater flexibility and more deployment options.
Cloud Services
Most cloud computing services fall into four categories:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the most basic category of cloud computing services. IaaS allows you to rent IT infrastructure, such as servers, networks, and data storage, from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis. IaaS allows you the highest level of flexibility and management control over your IT resources.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. The service provider hosts the hardware and software on its own infrastructure, so you don’t have to worry about managing these components separately.
- Serverless Computing also focuses on building app functionality without spending time managing the infrastructure. The biggest difference between PaaS and serverless computing is that serverless applications scale instantly, but they tend to offer less control over the deployment environment.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) includes an entire application stack that’s completely run and managed by the service provider. Since the provider manages the full application workload, all you need to worry about is how you’ll use the software.
Cloud Security
As you move beyond general familiarity with the leading cloud platforms, it’s important for you to prioritize cloud security.
Make sure you choose a trusted cloud provider and read your Service Level Agreement (SLA) carefully to understand what your responsibilities are as the user.
You can also prioritize cloud security by regularly monitoring your cloud environment, implementing a Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) solution, and training your users on cybersecurity best practices.
Step 5. Focus on System and Network Administration.
One of your most important jobs as an IT director is ensuring that your company’s computer systems and networks are operating smoothly. You might even fill the role of your organization’s system or network administrator.
Understanding the skills surrounding systems and networks will enable you to more effectively manage your IT department while reducing downtime for your organization.
Operating System (OS) Administration
First, you need a solid understanding of different Operating Systems (OS). Windows and Linux operating systems have long been embraced and are a good place to start with, but other systems, such as macOS, are gaining popularity. Your industry might favor a particular OS, so it’s a good idea to be familiar with which systems are most popular.
Here’s a list of the most common operating systems that you should be familiar with:
- Windows
- Linux
- macOS
- Android
- iOS
Installing and Configuring Hardware and Software
System administrators spend a lot of time working with physical devices, like servers and printers. Your job might include implementing automated software solutions and replacing any outdated hardware or software components.
Knowledge of Networks
When working as a system or network administrator, you’ll be expected to set up and maintain a variety of networks, such as Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), Storage Area Networks (SANs), and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
It’s also helpful to have experience setting up network security features, like firewalls.
Consult with a VCIO
A Virtual Chief Information Officer (vCIO) is a valuable resource who can provide additional feedback surrounding system and network administration.
Here are just a few areas in which a vCIO can support your organization:
- Working with you to develop IT strategies
- Connecting IT strategies to business goals
- Creating a customized IT roadmap
- Developing an IT budget
- Initiating IT project planning and management
- Continuing consulting and education with in-house security teams

Step 6. Delve into Data Analytics.
The ability to analyze data is useful in a variety of IT tasks. And as an IT director, it will be especially important for you to transform raw data into feedback that will guide decision-making.
Database Administration
While data analytics focuses on studying company data to aid in problem solving and decision making, database administrators oversee data management as a whole. This includes securing the data, managing user access, implementing backup and recovery solutions, retrieving lost data, and providing any necessary user training.
In some cases, one person will handle the responsibilities of both a data analyst and a database administrator. A database administrator will also work with programmers to plan, implement, and design database solutions.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the process of translating raw information into a visual context. Data sets can be complex and hard to understand, so it’s your job to represent the data in a way that makes sense for other members of your organization.
Visuals are an effective way to tell the story of what the data means and why stakeholders should care. Data visualization also helps guide decision-making across the organization.
Big Data
Some data sets are larger and more complex than others, and they can be so voluminous that traditional data processing software can’t manage them.
However, these massive volumes of data can provide insight that will guide decision-making and future business strategies.
Learning how to analyze big data can help you solve some of your organization’s biggest problems—which will lead to future opportunities and growth within your career.
Quality Assurance
For companies in the retail industry, data analytics is essential identifying issues and opportunities within their products and merchandise.
Quality assurance associates rely on data analytics to make sure processes are performed correctly and that products meet the expectations of customers.
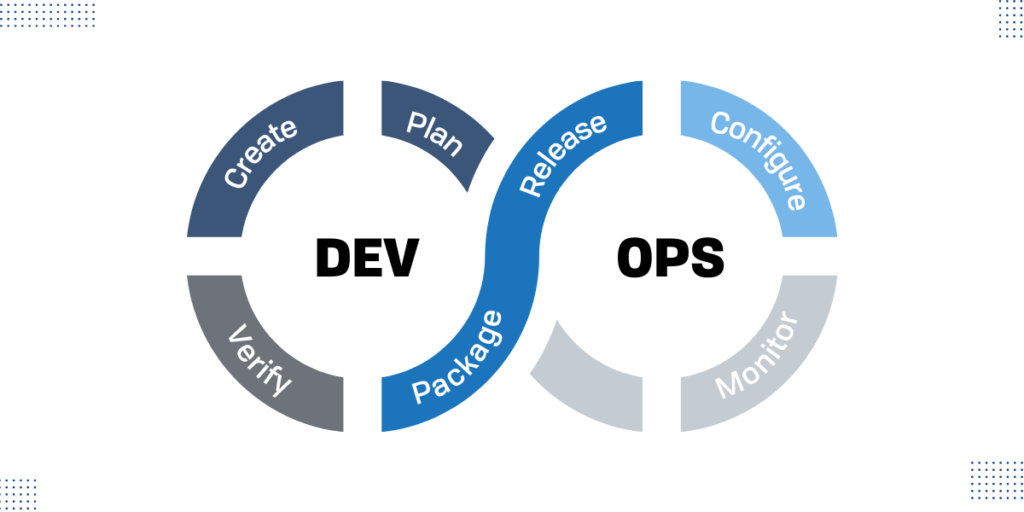
Step 7. Implement the DevOps Methodology.
DevOps enables software developers (devs) and operations (ops) teams to accelerate the process of building and delivering secure software.
While DevOps deals specifically with software development, understanding DevOps principles will improve the culture of your IT department and allow you to complete tasks more efficiently.
The DevOps methodology consists of four key principles that guide the efficiency of application development and deployment.
- Automation of the software development life cycle
- Collaboration and communication between development and operations teams
- Continuous improvement and minimization of waste
- Hyperfocus on user needs with short feedback loops
Think about ways that you can adopt these principles within your IT department. How can you prioritize cross-team communication? Are there any tasks within your workflow that you can automate? How can you make your toolsets more cohesive?
By establishing the DevOps methodology within your organization, you’ll improve the effectiveness of your IT department while also enhancing the culture of your organization as a whole.
Step 8. Fine-Tune Your Project Management Skills.
Project management skills are applicable in a variety of situations. They will make you better at your job as an IT director, regardless of the size of projects you’re managing.
Understanding project management methodologies and applying them to your processes will add efficiency and effectiveness to your workflow.
Scheduling and Time Management
One of the most common causes of project failure is poor planning.
Learning how to juggle multiple schedules and anticipate potential roadblocks will increase your chances of delivering successful projects.
Developing a project plan that captures the necessary requirements and scope will also go a long way in saving time and money.
Risk Management
Risk management goes hand in hand with time management, as it helps you avoid unnecessary delays and missed deadlines down the road.
The core of risk management is identifying and planning for potential risks within a project, thus avoiding major problems that might otherwise derail a project.
Knowledge of Project Management Methodologies
Although time and risk management are fundamental to your role as a project manager, it’s also important for you to understand the fundamental project management methodologies.
Many of these methodologies are industry-specific and require certification, so make sure you do your research.
Here are some of the most common project management methodologies:
- Agile
- Scrum
- Waterfall
- Lean
- Six Sigma
- PRINCE2
Proficiency with Project Management Software
Finally, having a working knowledge of project manager software will save you time and money in the long run.
There are many project management software options available, so determine which tools and features are most important to the needs of you and your team.
Consult with an Expert
Handling project management on your own can be overwhelming.
Luckily, there are experts available who can help you develop and complete projects in app development, web development, cybersecurity, SQL, and more!
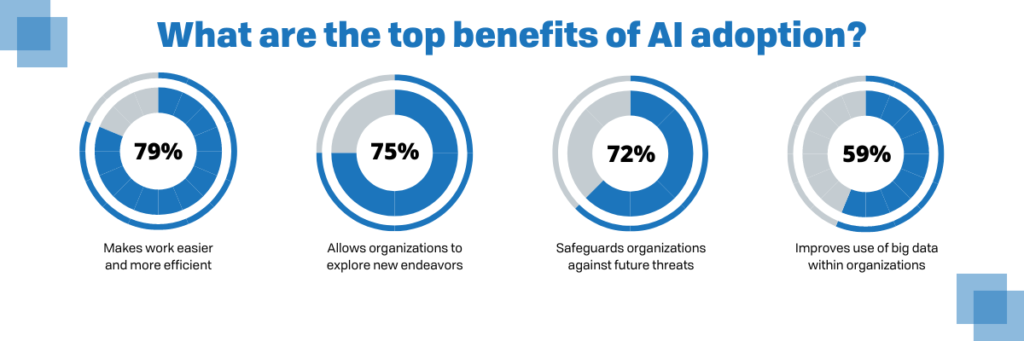
Step 9. Become Familiar with Artificial Intelligence (AI).
With new technological discoveries made every year, it’s no surprise that Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are becoming more and more sophisticated.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning that teaches computers how to learn by example. By processing large amounts of data, computer models learn to classify images, text, and sound.
There are countless applications for deep learning.
- Automated vehicles rely on deep learning to automatically detect street lights, stop signs, and pedestrians.
- Cancer researchers are using deep learning to accurately identify cancer cells.
- And smart speakers rely on speech translation and voice recognition powered by deep learning applications.
Signal Processing Techniques
Signal processing is a branch of electrical engineering used to model and analyze signals, such as sound, images, and scientific measurements.
There are a variety of applications for signal processing, including speech recognition, image processing, audio signal processing, wireless communication, and source coding techniques.
Neural Network Architecture
Neural networks are a part of deep learning that mimic human-brain behavior to solve complex problems. They’re used for adaptive control, predictive modeling, pattern recognition, data processing, regression analysis, and trainable applications.
Neural networks also find applications in other fields like marketing and healthcare.
Distributed Computing
Distributed computing is a branch of computer science where multiple software components are situation on various computers but run as a single system.
Examples of distributed computing include telecommunication networks, multiplayer online video games and peer-to-peer applications.
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis is the method of categorizing or grouping objects. Clustering can be performed manually or by algorithms, depending on efficiency.
This skillset is often used in statistical data analysis for applications, such as pattern recognition, data compression, image analysis, and computer graphics. In computer science, clustering is often used in software development, anomaly detection, and natural language processing.
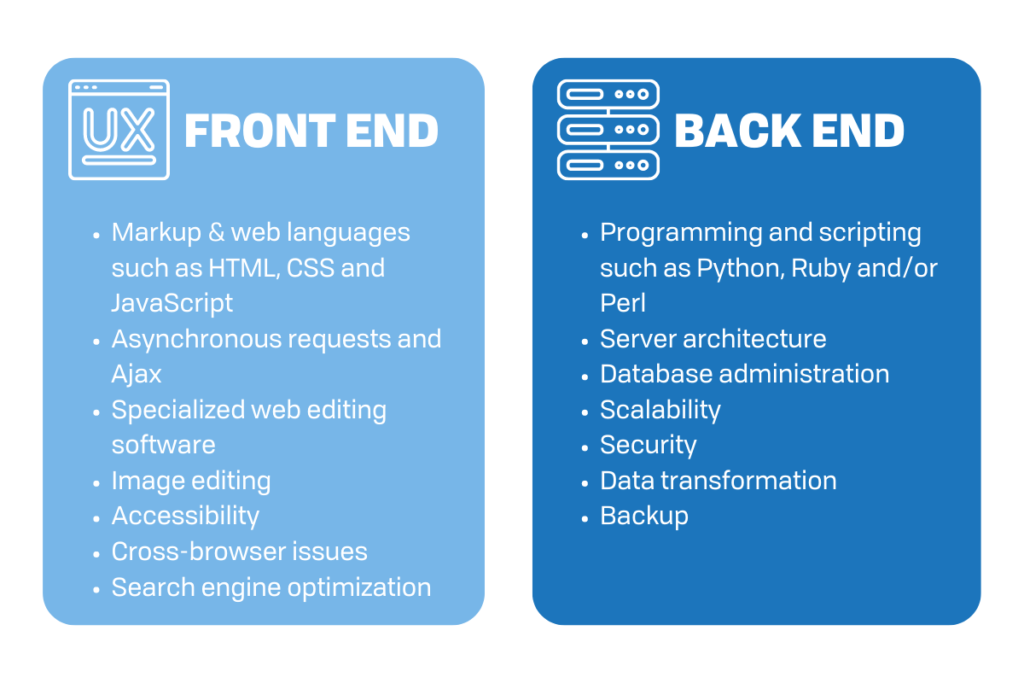
Step 10. Learn Web Development.
As the administrator for your company’s website, you’ll need to understand the basics of web development and how to overcome common obstacles.
Back-End Web Development
First, learn all you can about the back end of web development.
Your experience in programming will start you off on the right track, but here are some other skills that will be helpful to delve into:
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
- Functional Programming
- Structured Query Language (SQL)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
One of the more cost-effective ways to increase traffic to your organization’s website is through Search Engine Optimization (SEO). And this branch of ecommerce relates more directly to IT than perhaps any other subset of marketing.
Learning just a few of the fundamentals of SEO will make a huge difference in your organization’s website performance.
User Experience (UX)
User Experience (UX) encompasses all aspects of the end user’s interaction with a company, its services, and its products.
Learning to anticipate your customer’s needs and catering your services towards solving their problems will elevate your user experience and create a better reputation for your company.
Testing and Debugging
Once your website goes live, you’ll need to set aside time for regular testing to ensure that your code is functioning correctly.
When problems arise, you must be able to debug them. The ability to troubleshoot a variety of issues and resolve problems quickly will keep your downtime low and ensure that your customers can access the information they need from your website.
Conclusion
There are dozens of skills right at your fingertips that will transform your abilities as an IT director.
Start today by meeting with an IT consultant to learn which skills will set you apart from the masses and provide the greatest benefit to your organization.
As you invest in meaningful skills, you’ll be better prepared to demonstrate your expertise and the value of your IT team to the leaders of your organization.
Blog & Media
Cloud Services
Managed IT Support
Cyber Security
Project Services
Servers/Infrastructure
Firewalls
Networking
Hardware/Software
Microsoft Products/Cloud
Amazon Web Services
Penetration Testing vs Vulnerability Scanning
If you’re responsible for managing the security of your organization’s network or systems, you may have heard the terms “penetration testing” and “vulnerability testing” thrown
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Your organization can’t afford to neglect backup and disaster recovery. If it takes your business too long to get back online after a disaster, you
6 Steps to Secure Customer Data
Securing customer data is essential for one major reason: your business depends on it. As an IT director, you recognize the importance of cybersecurity when
5 Steps to Promote Compliance in the Workplace
You’re familiar with the ever-changing world of regulatory compliance. Robust compliance enables you to avoid legal liabilities while improving your organization’s effectiveness. And many of

